Versionize a Platformatic application
Introduction
Platformatic applications support versioning of the API without the need to deploy a new application for each version. Every time you bump a new API version of your application platformatic calculates the diff between the previous and current versions and maps API routes to the current one. In cases when it's not possible to automatically map the routes, platformatic generates a mapper plugin that can be used to map the routes manually or generated automatically by OpenAI. As a result, you have a single instance of the application that handles all the requests.
Setup platformatic application versioning
Setup the application
Lets start with a basic platformatic service application that can be generated by running create-platformatic command.
npx create-platformatic@latest
Lets add a new route to the application that will be used to test the versioning. Add the following code to the routes/root.js file.
fastify.get('/users', {
schema: {
response: {
200: {
type: 'array',
items: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
id: { type: 'number' },
name: { type: 'string' }
}
}
}
}
}
}, async (request, reply) => {
return [
{ id: 1, name: 'Larry Lute' },
{ id: 2, name: 'Marcus Miller' },
{ id: 3, name: 'Devin Booker' }
]
})
It's important to add the schema property to the route definition. Platformatic uses the OpenAPI schema to find the differences between the versions.
You can start the application and test that the route is working as expected.
npx platformatic@latest start
Testing /users route:
curl http://localhost:3042/users
Response:
[
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Larry Lute"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "Marcus Miller"
},
{
"id": 3,
"name": "Devin Booker"
}
]
Bump the first API version
Now when we have a basic application we can bump the first API version. To do that we need to run the following command:
npx platformatic@latest service versions bump
It will create a first version of the application v1 and will map all the routes to the current version. If you start the application, you will see that now the route is available under the /v1/users path. If you want to create a different version name you can use the --version option.
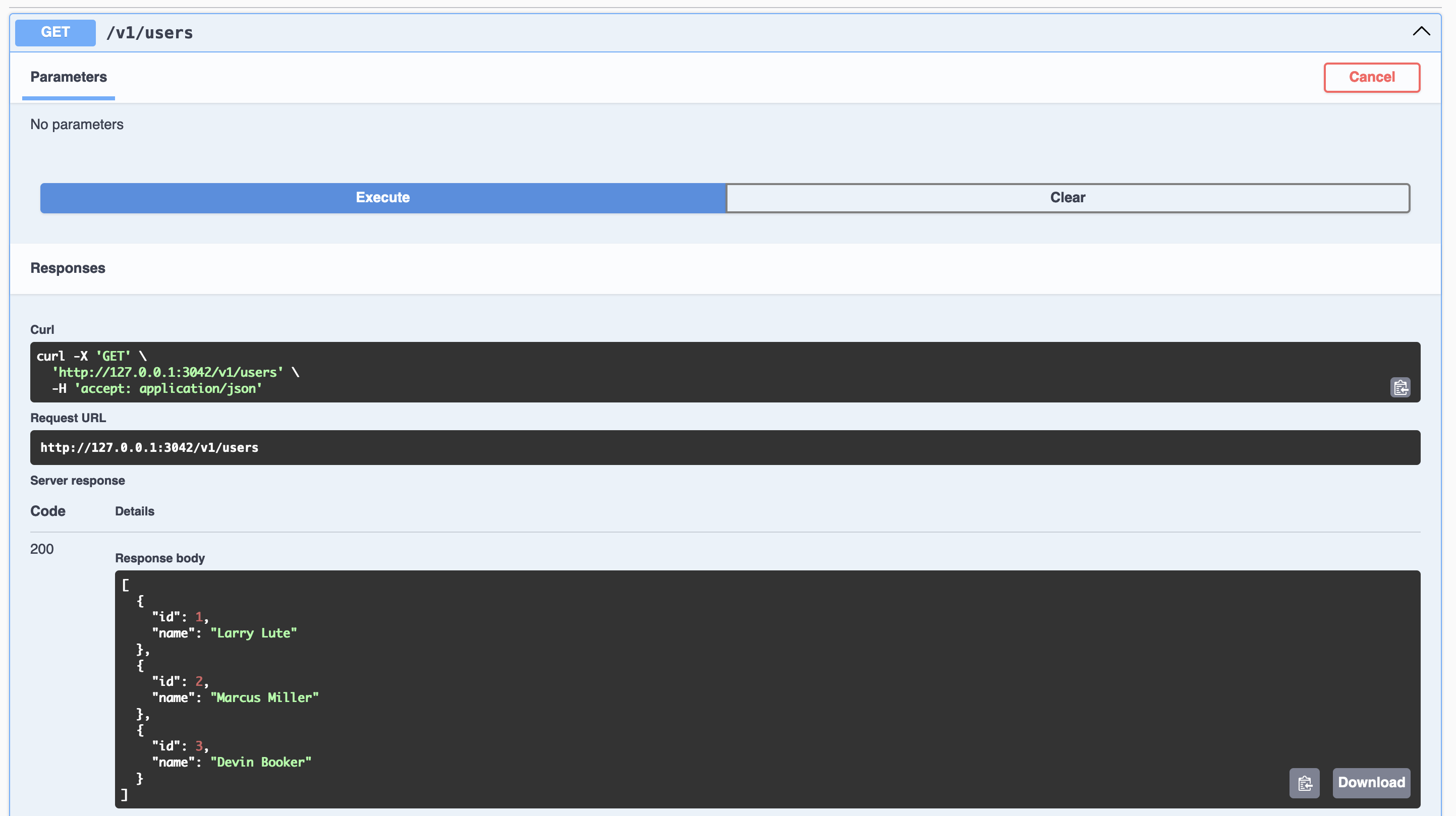
Testing /v1/users route:
curl http://localhost:3042/v1/users
[
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Larry Lute"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "Marcus Miller"
},
{
"id": 3,
"name": "Devin Booker"
}
]
API "v1" swagger page
Bump the second API version
Now when we have the first version of the application we can bump the second version. To do that we need to run the same command as before:
npx platformatic@latest service versions bump
It will create a second version of the application v2 and will map all the routes to the current version. If you start the application, you will see that now the same under /v1/users and /v2/users paths. These routes were mapped automatically because the OpenAPI schema was the same for both versions.
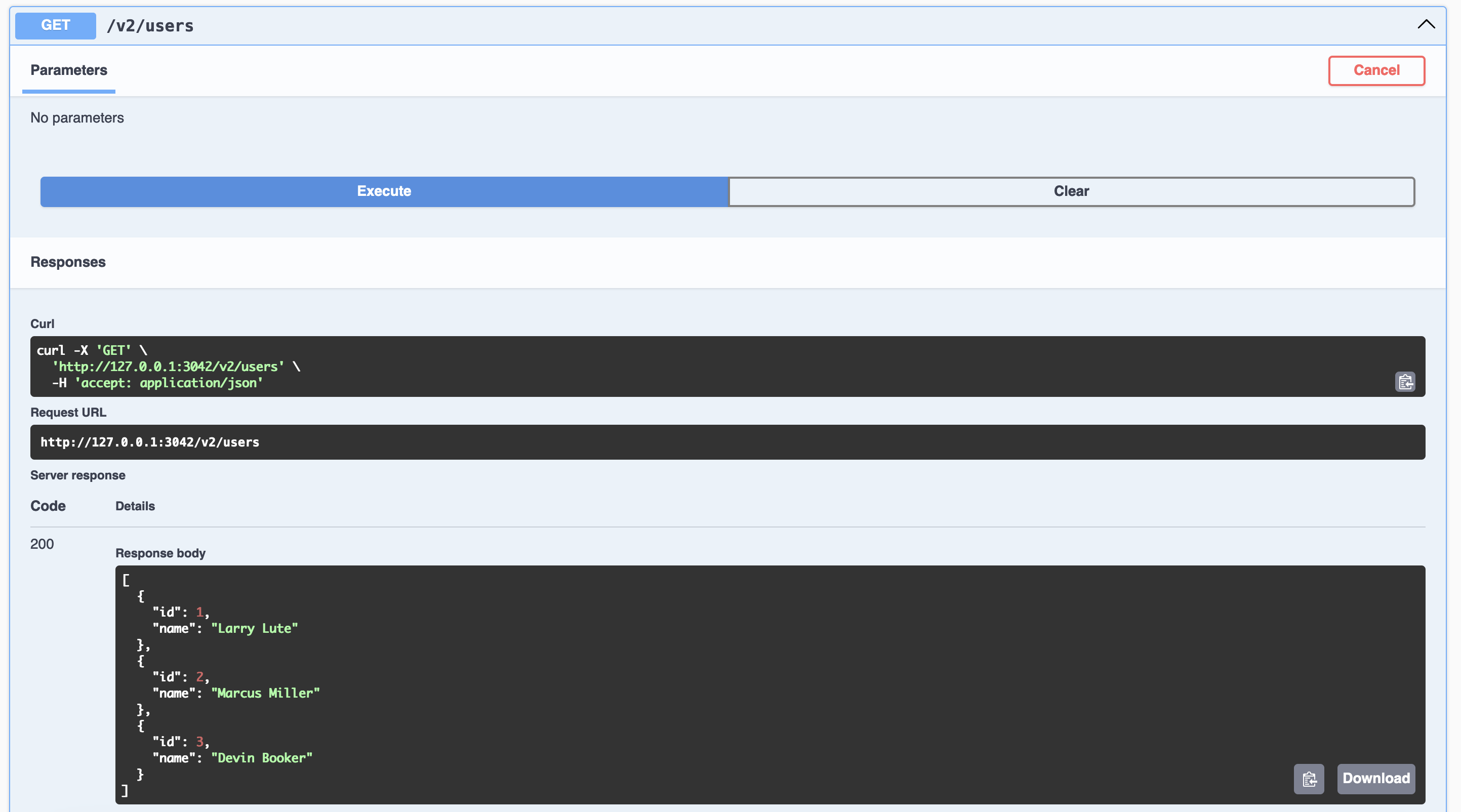
Testing /v2/users route:
curl http://localhost:3042/v2/users
[
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Larry Lute"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "Marcus Miller"
},
{
"id": 3,
"name": "Devin Booker"
}
]
API "v2" swagger page
Update the second API version
Lets make some changes to the latest version of the application. Lets modify the /users route in a following way:
fastify.get('/users', {
schema: {
response: {
200: {
type: 'array',
items: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
id: { type: 'number' },
firstName: { type: 'string' },
lastName: { type: 'string' }
}
}
}
}
}
}, async (request, reply) => {
return [
{ id: 1, firstName: 'Larry', lastName: 'Lute' },
{ id: 2, firstName: 'Marcus', lastName: 'Miller' },
{ id: 3, firstName: 'Devin', lastName: 'Booker' }
]
})
Now the route returns the firstName and lastName instead of the name. Lets update the second version of the application to reflect the changes. To do that we need to run the following command:
npx platformatic@latest service versions update
Having that now the second version of the route can't be mapped automatically, platformatic will generate a mapper plugin that can be used to map the routes manually or generated automatically by OpenAI. The mapper plugin will be generated in the versions/v1/get-users.js file.
In the mappers plugin you can find a lot of useful information about the changes and code that proxies the "v1" route to the "v2" route. All you need to do is to update the mapOutputData200 function to map the response from the "v2" route to the "v1" route.
function mapOutputData200 (outputData) {
const mappedBody = outputData.responseBody.map((user) => {
return {
id: user.id,
name: `${user.firstName} ${user.lastName}`
}
})
return {
headers: outputData.headers,
responseBody: mappedBody
}
}
Now when you start the application and see that the /v1/users route returns response with the name property when the /v2/users route returns response with the firstName and lastName properties.
Testing /v1/users route:
curl http://localhost:3042/v1/users
[
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Larry Lute"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "Marcus Miller"
},
{
"id": 3,
"name": "Devin Booker"
}
]

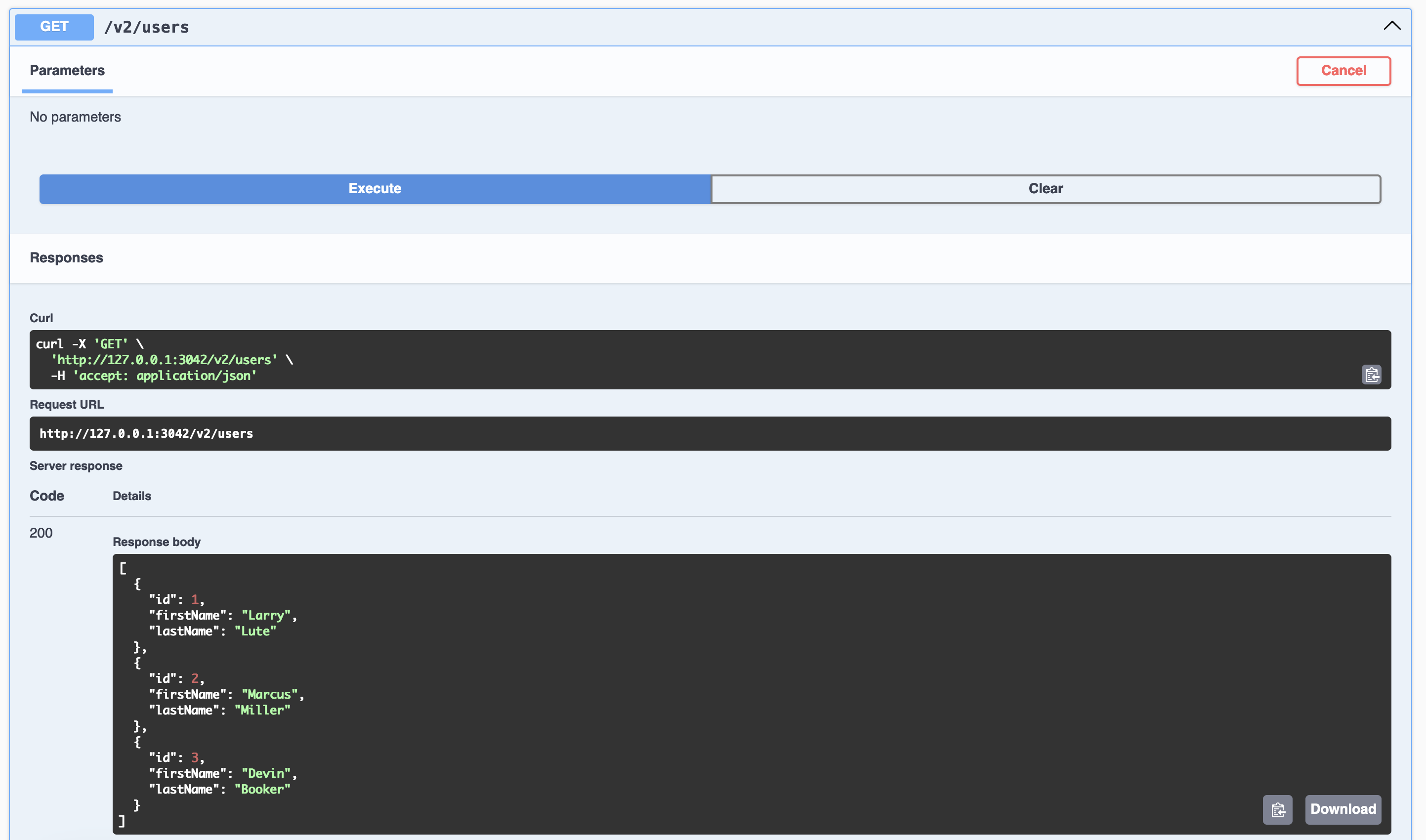
Testing /v2/users route:
curl http://localhost:3042/v2/users
[
{
"id": 1,
"firstName": "Larry",
"lastName": "Lute"
},
{
"id": 2,
"firstName": "Marcus",
"lastName": "Miller"
},
{
"id": 3,
"firstName": "Devin",
"lastName": "Booker"
}
]
API "v2" swagger page
Generating the mapper plugin with OpenAI
Platformatic supports generating the mapper plugin automatically using the OpenAI. Before doing so, make sure you have a platformatic user API key. If not, you can generate it by running the following command:
npx platformatic@latest login
Now when you have the API key you can generate the mapper plugin by running the following command:
npx platformatic@latest service versions update --openai
It will update the same mapper plugin as before but this time it will use OpenAI to generate the request and response mappers. You should always be careful and check the generated code. In my case OpenAI generated the following code for the same mapOutputData200 function:
// !!! This function was generated by OpenAI. Check before use !!!
function mapOutputData200 (output) {
const mappedOutput = {
headers: {},
responseBody: output.responseBody.map(item => ({
id: item.id,
name: `${item.firstName} ${item.lastName}`
}))
}
return mappedOutput
}
As you can see the code is a little bit different but the result is the same. You can use the code generated by OpenAI or write your own.
Shared routes
Sometimes you may want to have a route that is shared between all the versions. For example, you may want to have a /health route that is available under all the versions. To do that you need to set the plugin with this route in the platformatic plugins config section rather than in the versions config section.